PRODUCT
Tel:400-685-8582
Tel:+86-21-57715555
+86-21-37831986
Fax:+86-21-37831846
Phone:13817716438
Email:weho@chinaweho. com
Address:Building 2, No.8 Nanle Road, Songjiang District, Shanghai
Voltage Regulator Classification Voltage Regulator Principle Voltage Regulator Parameters Voltage Regulator Function
Time:2021-05-26 View:714
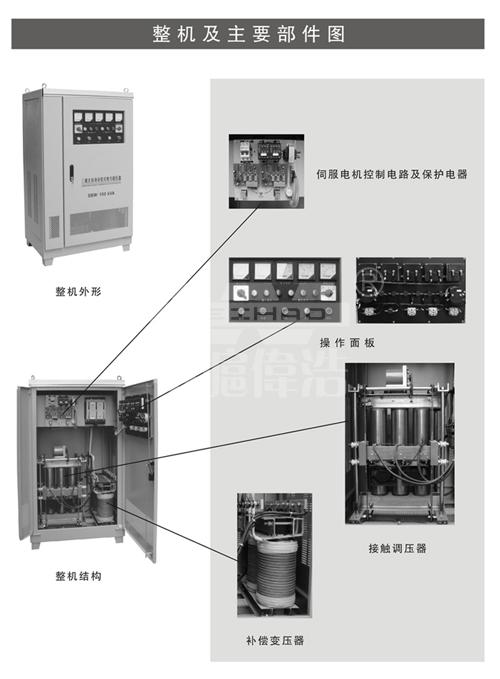
Introduction to the regulator;
It is a power supply circuit or power supply equipment that can automatically adjust the output voltage. Its function is to stabilize the power supply voltage that fluctuates greatly and does not meet the requirements of electrical equipment within its set value range, so that various circuits or electrical equipment can be Work normally under the rated working voltage.
Voltage stabilizers include: large AC voltage stabilizers ranging from tens to thousands of kilowatts, which are the working power supply for large-scale experiments and industrial and medical equipment. There are also small AC voltage stabilizers of several watts to several kilowatts, which are used to provide high-quality power for small laboratories or home appliances. The initial power voltage stabilizer relies on the beating of the relay to stabilize the voltage. When the grid voltage fluctuates, the automatic correction circuit of the power regulator is activated to make the internal relay operate. Forcing the output voltage to remain near the set value, the advantage of this circuit is that the circuit is simple, but the disadvantage is that the voltage regulation accuracy is not high, and every time the relay jumps and shifts, it will cause an instantaneous interruption of the power supply and spark interference. This greatly interferes with the reading and writing work of computer equipment, and it is easy to cause error signals in the computer, and in severe cases, the hard disk will be damaged. At present, most of the high-quality small voltage stabilizers use the method of motor-driven carbon brush to stabilize the voltage. This voltage stabilizer has little interference to electrical equipment and has relatively high voltage stabilization accuracy.
working principle:
Since some electrical appliances contain coil components, eddy currents that hinder the current will be generated at the initial stage of power-on. The generation of eddy currents will not only weaken the instantaneous voltage when the electrical appliances are started, resulting in slow startup, but also strengthen the instantaneous voltage generated after the circuit is broken, which may cause spark damage. circuit. At this point, a voltage regulator is needed to protect the normal operation of the circuit. The voltage regulator consists of a voltage regulator circuit, a control circuit, and a servo motor. When the input voltage or load changes, the control circuit performs sampling, comparison, and amplification, and then drives the servo motor to rotate, so that the position of the voltage regulator carbon brush changes. By automatically adjusting the coil turns ratio, the output voltage is kept stable. The voltage stabilizer with larger capacity also works on the principle of voltage compensation.
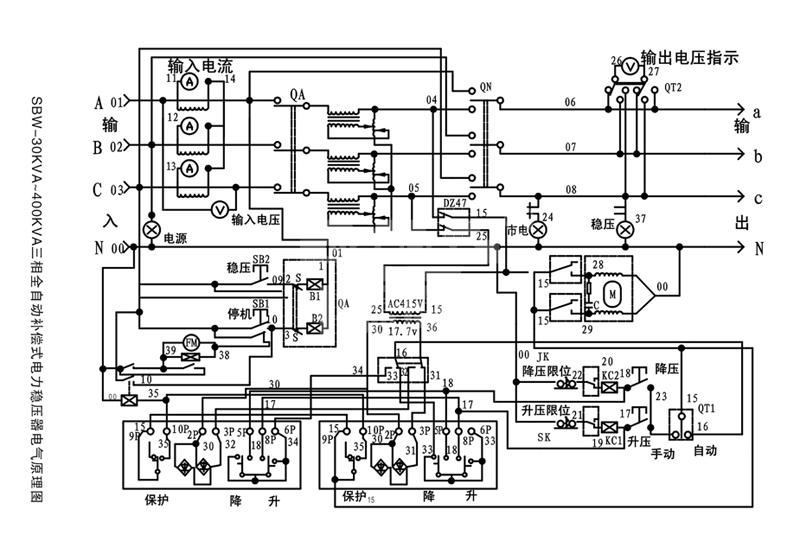
effect:
With the rapid advancement of society, the number of electrical equipment is increasing day by day. However, due to the aging and development of power transmission and distribution facilities, as well as poor design and insufficient power supply, the voltage of end users is too low, while the voltage of line users is often too high. Sophisticated equipment, like a time bomb. As a public power grid, the mains system is connected to thousands of various loads. Some of the larger inductive, capacitive, switching power supplies and other loads not only obtain power from the power grid, but also cause damage to the power grid itself. Affect and deteriorate the power supply quality of the power grid or local power grid, resulting in the distortion of the mains voltage waveform or frequency drift. In addition, unexpected natural and man-made accidents, such as earthquake, lightning strike, open circuit or short circuit of power transmission and transformation system, will endanger the normal supply of electricity, thus affecting the normal operation of the load. Unstable voltage will cause fatal injury or wrong operation of the equipment, affect production, cause delay in delivery, unstable quality and other losses. At the same time, it accelerates the aging of the equipment, affects the service life and even burns the accessories, so that the owner faces the trouble of needing maintenance or needs to update the equipment in a short period of time, wasting resources; in severe cases, safety accidents even occur, resulting in immeasurable losses. According to the tests of electric power experts,
The problems that often occur in the power grid and cause interference or damage to computers and precision instruments mainly include the following:
1. Power surges: Refers to the rms value of the output voltage being 110% higher than the rated value and lasting for one or several cycles. Surge is mainly due to the high voltage generated by the sudden unloading of the grid when the large electrical equipment connected to the grid is shut down.2. High voltage spikes: refers to the voltage with a peak value of 6000v and a duration from 1/10,000th of a second to 1/2 cycle (10ms). This is mainly due to lightning strikes, arcing, static discharges or switching operations of large electrical equipment.
3. Switching transients: refers to the pulse voltage with a peak voltage of up to 20000V, but the duration is between one millionth of a second to one ten thousandth of a second. The main causes and possible damage are similar to high voltage spikes, only the solution is different.
4. Voltage sag (power sags): refers to the low-voltage state in which the effective value of the mains voltage is between 80% and 85% of the rated value, and the duration is one to several cycles. Power large equipment, large motor starting, power transformers or large access may cause the problem
5, wires noise (electrical line noise): refers to radio frequency interference (RFI) and electromagnetic interference (EFI), and various other high frequency interference . The operation of the motor, the action of the relay, the operation of the motor controller, the broadcast emission, the microwave radiation, and the electrical storm, etc., can cause line noise interference.
6. Frequency variation (frequency variation): refers to the variation of the mains frequency exceeding 3Hz. This is mainly caused by the unstable operation of the emergency generator, or by the power supply with unstable frequency. Therefore, the use of voltage regulators is essential for electrical equipment, especially high-tech and precision equipment with strict voltage requirements.
The main technical parameters:
Project Single-phase three-phase (three-phase four-wire system, separate regulation)voltage regulator input voltage range 160V ~ 250V phase voltage 160V ~ 250V, line voltage 280V ~ 430V, voltage regulator output voltage 220V or 110V, phase voltage 220V Line voltage 380V
regulator overvoltage protection value 246V±4V phase voltage 246V±4V (subject to phase voltage), line voltage 426V
regulator voltage regulation accuracy ±1~3%
A. The regulator has an input voltage adaptation Scope. The IEC standard is that the input voltage changes within the range of ±10% of the rated value. If it exceeds the range, it will automatically sound and light alarm and the output voltage cannot be stabilized within the required range.
B. The output voltage regulation rate is the output voltage caused by the change of the input voltage. When the load is at the rated value, the input voltage is adjusted upward from the rated value to the upper limit value and the lower limit value according to the source voltage range, and the maximum change (±?) of the output voltage is measured. The smaller the value, the better, and it is an important indicator to measure the performance of the AC voltage stabilizer.
C. Load regulation rate: It is the effect of the change of the load caused by the change of the output. Change the load current and measure the change (±?) of the output voltage. The smaller the value, the better, and it is also an important indicator to measure the performance of the AC voltage stabilizer.
D. The relative harmonic content of the output voltage (also known as the output voltage distortion), usually expressed by THD, is the ratio of the total effective value of the harmonic content to the fundamental effective value. When the load is rated, the input voltage distortion meets the reference Under conditions (generally should be less than 3), measure the output voltage distortion when the input voltage is the lowest value, rated value and highest value, whichever is the largest. The smaller the value, the better.
E. Efficiency: is the output active power P0 Ratio (percentage) to the input active power Pi,
F. Load power factor, the capacity of the voltage stabilizer is expressed in volt-ampere (VA) or kilovolt-ampere (KVA) value. In addition to pure resistive load, there are also inductive and capacitive loads in the load, that is, in addition to active power in the load. In addition to power, there is reactive power. This pointer reflects the ability of the AC regulated power supply to carry inductive and capacitive loads. In general AC regulated power supply, the load power factor cosφ is 0.8. When the product is 1KW, the output active power (that is, the capacity of the resistive load) is up to 800W. If the product is expressed by 1KW (cosφ is still 0.8), it can be The output active power is 1KW, and the output power at this time is S=1000/0.8=1250VA. When the value of the load power factor is small, it means that the power supply equipment has a strong ability to adapt to reactive loads.
G. The parameters of the AC voltage stabilizer include output power, input frequency, source frequency effect, random deviation (time drift), no-load input power, source power factor (this value is different from the load power factor, and it is hoped that the bigger the better, the maximum For 1), the relative harmonic content of source current, audio noise and other three-phase AC stabilized power supply, as well as three-phase output voltage unbalance, etc. The definition and test method of these instructions can refer to relevant standards.
The scope of application of the voltage stabilizer:
The voltage stabilizer can be widely used in: electronic computers, precision machine tools, computed tomography (CT), precision instruments, test devices, Elevator lighting, imported equipment and production lines and other places that require stable voltage of the power supply. It is also suitable for users at the end of the low-voltage distribution network where the power supply voltage is too low or too high, and the fluctuation range is large, and the electrical equipment with large load changes, especially suitable for all voltage-stabilized electricity places that require high grid waveforms. The high-power compensation type power stabilizer can be connected to thermal power, hydraulic power and small generators.Voltage stabilizer product classification:
According to the different output properties of the voltage stabilizer, the voltage stabilizer is generally divided into two categories: AC voltage stabilizer (AC stabilized power supply) and DC voltage stabilizer (DC stabilized power supply). The following focuses on the introduction of DC regulated power supply, referred to as regulated power supply. According to the working state of the adjustment tube, the regulated power supply is often divided into two categories: linear regulated power supply and switching regulated power supply. In addition, there is a small power supply that uses a Zener tube.Switching Regulators:
Switching regulators use an output stage that repeatedly switches "on" and "off" states to produce an output voltage along with energy storage components (capacitors and inductors). Its adjustment is achieved by adjusting the switching timing based on feedback samples of the output voltage. In a fixed frequency regulator, the switching timing is adjusted by adjusting the pulse width of the switching voltage, which is called PWM control. In a gated oscillator or pulse-mode regulator, the width and frequency of the switching pulses are kept constant, however, the "on" or "off" of the output switch is controlled by feedback. Depending on the arrangement of switches and energy storage components, the resulting output voltage can be greater or less than the input voltage, and a single regulator can be used to generate multiple output voltages. In most cases, pulsed (buck) switching regulators convert power more efficiently than linear regulators for the same input and output voltage requirements. Compensation type---high-precision AC compensation type stabilized power supply (single-phase 0.5kVA and above, three-phase 1.5kVA and above) with compensation transformer and 110V output.
Parametric Regulator:
Linear Regulator
LDO is a linear regulator. Linear regulators use transistors or FETs operating within their linear region to subtract excess voltage from the applied input voltage to produce a regulated output voltage. The so-called drop voltage refers to the minimum value of the difference between the input voltage and the output voltage required by the regulator to maintain the output voltage within 100mV of its rated value. LDO (low dropout) regulators with positive output voltage typically use a power transistor (also known as a pass-through device) as the PNP. This transistor is allowed to saturate, so the regulator can have a very low dropout voltage, typically around 200mV, compared to around 2V for traditional linear regulators using NPN compound power transistors. The negative output LDO uses an NPN as its pass device and operates similarly to the positive output LDO's PNP device. Newer developments use CMOS power transistors, which provide the lowest dropout voltage. With CMOS, the only voltage drop across the regulator is due to the ON resistance of the power supply's load current. If the load is small, the voltage drop generated in this way is only tens of millivolts.Regulator error flags:
The error flag is an open collector output that sends a signal to the regulator when the regulated output voltage falls below 5% (typical) of the rated output voltage. Initially, the error is marked low until the output voltage reaches 95% of the rated output voltage. In some cases, there is a delay in the flagging of errors that occur during power transitions. This delay is set by an external capacitor and can be used as a power-on reset function to reset the microprocessor to power-up. If the state "ERROR" is displayed, the low output voltage condition makes the open collector output high (the marker transistor displays OFF). This flag output is low when the output voltage is within 5% of the rated voltage.Regulator On/Off or Shutdown:
An "on/off" or "shutdown" function enables the voltage regulator to be turned on or off while it is energized. Although in "off" or "shutdown" mode, the regulator's supply current is reduced to a lower level because the output is disabled, but the internal bias circuit is still running. When re-enabled, the regulator will re-regulate the output voltage much faster than if the input voltage were turned off and on. If displayed in the "on" state, the regulator will be activated by logic high. Otherwise, it will be activated by a logic low level.Regulator synchronization or frequency adjustment:
In switching regulators and switched capacitor converters, an internal oscillator is used to set the switching frequency of the output transistors. The value of this switching frequency can determine certain external components used in the converter, determine the frequency of noise generated by the converter, and affect the performance of the converter. Some converters allow the switching frequency to be changed by adjusting the internal oscillator frequency ("frequency adjustment") or by synchronizing the oscillator with an external power supply ("synchronizing"). In general, by increasing the switching frequency, smaller components (capacitors, inductors) can be used in the converter output stage. This can reduce the efficiency of the converter due to increased switching losses unless higher quality components are also used. A well-performing higher frequency converter will have a faster transient response than a lower frequency converter. If you have several converters on a board, it is usually best to sync them to a common source. This controls the noise generated by the entire batch and minimizes any "tapping frequency" that may be generated. This issue is often important for high power converters (eg 5W or higher). In many cases, the switching frequency can only be increased from its preset value. The product data sheet will indicate the frequency range for this function.Voltage stabilizer selection method
Capacity safety factor:
The AC regulated power supply takes the output apparent power (kVA) as the nominal rated capacity, and in general, the load is not purely resistive, that is, the power factor COS¢≠1, the active power that the regulator can actually output kW= Capacity (kVA) × COS¢. Therefore, in the actual selection, the regulated power supply should be reasonably selected according to the specific conditions of the rated power, power factor and load type of the electrical equipment, and an appropriate margin should be reserved for its output power, especially when the impact load is selected. To be larger, the safety factor of the type of load equipment selects the capacity of the regulated power supply, and the pure resistive load such as incandescent lamps, resistance wires, electric furnaces and other equipment is 1.25~1.5 1.25~1.5 times the total load power. Inductive and capacitive loads such as fluorescent lamps, fans, motors, pumps, air conditioners, computers, refrigerators, etc. 2 ~ 3 ≥ 2 ~ 3 times the total load power. In the environment of large inductive and capacitive loads (such as motors and computers), the starting current of the load should be considered particularly large (up to 5~8 times of the rated current) when selecting the model, so the capacity of the voltage stabilizer should be selected according to the load power. 2.5~3 times. For example: 1 set of three-phase motor 2.2kW, 1 set of 5.5 kW, when selecting a voltage stabilizer, the capacity is greater than or equal to (2.2kW+5.5 kW) × 2.5=19.25 kVA, that is, at least three-phase SJW-20 kVA products must be selected. press.Output capacity curve of uncompensated regulated power supply:
Auto voltage regulator (single-phase 0.5kVA~3kVA, 10k horizontal and below, three-phase 9kVA and below) When the input phase voltage is lower than 198V, the output capacity begins to drop; when the input phase voltage is equal to 160V, it drops to 50% of the rated capacity of the regulator. Therefore, at the low end of the power supply voltage, special attention should be paid to reducing the load and derating, so as to avoid overloading and burning the voltage stabilizer; the auto-coupled voltage stabilizer can output two voltages of 220V and 110V at the same time. But even when all output is 110V, the load of the voltage stabilizer cannot exceed 50% of the rated capacity, otherwise it is overloaded.Voltage stabilizer installation and use;
1. Connect the input of the voltage stabilizer to the power distribution board, and install a fuse that matches the power of the instrument on the user power distribution board to ensure the safety of electricity use.
2. Connect the power supply of the electrical equipment to the output terminal of the instrument. Note that the rated input voltage value of the electrical equipment should be consistent with the output of the voltage stabilizer, and do not connect it wrongly.
3. Turn on the power switch of the voltage stabilizer first, and the working indicator light is on. Observe whether the indicated value of the voltmeter is normal. When the output voltage is normal, turn on the power switch of the electrical equipment, and the voltage stabilizer can automatically adjust the voltage and supply power normally.
4. When the electrical equipment is not used for a long time, please turn off the power switch of the electrical equipment to reduce power consumption and prolong the service life of the voltage stabilizer.
5. The voltage stabilizer shall not be overloaded. When the mains voltage is low, the output capacity is reduced, and the load of the voltage regulator should be reduced accordingly.
6. When selecting electrical appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, water pumps and other equipment with motor running, a voltage stabilizer with a capacity of more than 3 times should be selected to prevent the starting current of the equipment from exceeding the current of the voltage stabilizer fuse or the current of the overcurrent protection circuit breaker to stabilize the voltage. blown fuse or circuit breaker has tripped or the voltage drop is too great to work.
7. The wire connected to the voltage stabilizer should have enough surface to prevent heat generation and reduce voltage drop. Voltage stabilizers with a capacity of more than 2KVA are connected by terminals. A single copper wire should be used, and the terminal screws should be tightened as much as possible to prevent the connection from heating.
8. Whether it is a single-phase or three-phase voltage stabilizer, after all the input and output lines are connected, the power switch of the load should be turned off first, then the voltage stabilizer should be turned on, and the power switch of the load should be turned on after checking that the output voltage is normal.
The basic characteristics of the voltage stabilizer: automatic compensation type power voltage stabilizer;
Basic structure: The motor drives the carbon brush to slide between the winding turns of the self-coupling transformer to directly adjust the output voltage or adjust the output voltage through the compensation transformer. Advantages: strong load capacity, high work efficiency, small waveform distortion, and strong anti-interference ability of the power supply itself . Disadvantages: slow response time (≥1S), mechanical wear, regular maintenance, AC contactor and motor generate large noise during voltage regulation. Application: industry, agriculture, transportation, post and telecommunications, military, railway, scientific research Large-scale electromechanical equipment, metal processing equipment, production lines, construction engineering equipment, elevators, medical equipment, embroidery and textile equipment, air conditioners, radio and television, household appliances, lighting and other places that require voltage stabilization in the fields of culture and other fields.AC purification voltage stabilizer:
basic structure: adopt the method of combining sine wave energy distribution and filter, adjust the output voltage by adjusting the conduction angle of the primary loop thyristor. Advantages: high voltage stabilization accuracy ≤±1%, response Fast time ≤40ms, with spike filtering effect. Disadvantages: There is a phase shift between the output and the input voltage, there is a little waveform distortion (additional ≤ 3.5%), and some special loads (such as thyristor loads) are not ideal. Applications: precision electronic equipment, medical equipment, computer rooms, experiments room, product aging and testing.
Contactless AC voltage stabilizer:
basic structure: by switching one or more groups of thyristors when the voltage or current crosses zero, the compensation winding of one or more transformers in the compensation transformer group can be boosted, stepped down, and the primary Short circuit, or switch the tap of the self-coupling transformer to adjust the output voltage. Advantages: strong load capacity, high work efficiency, small waveform distortion, fast response time, and low noise. Disadvantages: the voltage regulation accuracy is not high, application: all places that need voltage regulation.
The basic structure of the parameter regulator:
The saturation characteristic of the iron core material is used to show that the output voltage is basically stable. Advantages: reliable operation, strong overload capacity, automatic protection when output is short-circuited, simple structure, large voltage regulation range, and strong anti-interference ability. Disadvantages: heavy, bulky, High price, high noise, high temperature of iron core, high requirement for input power operating frequency. Application: computer related products, medical monitoring system, program control system, automatic test equipment, radio and television equipment, post and telecommunications equipment, automatic plug-in machine, Production lines, printing equipment, plastic injection equipment, ATMs, SMT equipment, scientific research and testing, etc.The basic structure of magnetic amplified AC voltage stabilizer:
The output voltage is stabilized by changing the magnetic resistance of the magnetic amplification transformer connected in series in the primary circuit of the auto-coupling transformer. Advantages: high voltage regulation accuracy, fast response time; disadvantages: heavy weight, large volume, high price. Application: precision electronic equipment, Medical equipment, computer rooms, laboratories, product burn-in and testing.Intelligent purification voltage stabilizer:
SBW5B-YL single and three-phase purification power supply is an AC stabilized power supply integrating voltage stabilization and anti-interference. The intelligent purification voltage stabilizer not only has high voltage stabilization accuracy, high efficiency, fast response and reliability It has the characteristics of good performance, low noise, small size and light weight, and can effectively suppress the peak voltage and various noise interference in the power grid. It can be widely used in computers, copiers, audio and video equipment, medical equipment, metering equipment, industrial equipment, office equipment, electronic instruments and ideal power supply equipment for automatic control systems.
Voltage stabilizer use precautions and maintenance:
1. Avoid violent vibration, prevent the inflow of corrosive gases and liquids, prevent moisture and place it in a ventilated and dry place. Do not cover the fabric to hinder ventilation and heat dissipation.2. Please use a three-plug (grounded) socket. The grounding screw on the machine should be properly grounded, otherwise the case will be charged with a test pen. This is caused by the distributed capacitance induced electricity, which is a normal phenomenon. eliminate. If the casing is seriously leaking and the measured insulation resistance is less than 2MΩ, it may be that the insulation layer has been damp or the circuit and the casing are short-circuited.
3. The 0.5-1.5KVA low-power voltage stabilizer uses fuses for overcurrent and short-circuit protection, and the 2-40KVA voltage stabilizer functions as DZ47 circuit breaker for overcurrent and short-circuit protection. Check for excessive power usage.
4. When the output voltage exceeds the protection value (the phase voltage protection value is adjusted to 250V±5V at the factory), the regulated power supply will automatically protect, cut off the output voltage of the regulated power supply, and at the same time the overvoltage indicator light will be on, the user should immediately shut down to check the grid voltage or Voltage stabilization. If the voltage stabilizer is automatically powered off (with input but no output), check whether the mains voltage is higher than 28OV. If it is lower than 280V, check whether the voltage regulator is faulty. Use it after finding out the reason.
5. If the output voltage of the voltage stabilizer deviates more from 220V, please adjust the potentiometer on the control board until the output voltage is normal (the input voltage cannot be adjusted if the voltage does not reach the voltage stabilization range).
6. When the mains voltage is often at the lower limit (<150V) or upper limit (>260V) of the input voltage of the voltage stabilizer, the limit micro switch is often touched, which is prone to control failure. At this time, the voltage stabilizer cannot be adjusted or can only be adjusted up (or only down), so you should first check whether the micro switch is damaged.
7. Please keep the inside of the machine clean, dust will hinder the rotation between the gears and affect the output voltage accuracy. Please clean and maintain the contact surface of the coil in time. When the carbon brush is severely worn, the pressure should be adjusted to prevent the contact surface between the carbon brush and the coil from sparking. The carbon brushes should be replaced when the length is less than 2mm. When the coil plane flashover is blackened, it should be polished with fine sandpaper.
8. The input end of the three-phase voltage stabilizer must be connected to the neutral line (neutral line), otherwise the voltage stabilizer cannot work, and the voltage stabilizer and electrical equipment will be damaged. Do not use the ground wire instead of the neutral wire, and the neutral wire must not be connected to the fuse.
9. When the output voltage of the voltage stabilizer is lower than the rated voltage (220V or three-phase 380V), check whether the input voltage is too low. When the rated voltage is reached at no-load and the output is lower than the rated voltage when loaded, this is because the input line load surface is too small, the line voltage drop is too large under load, and the input voltage used is lower than the lower limit of the regulator's adjustment range, then it should be replaced Thicker input wires.
10. When the power of a single load is large (such as air conditioners, etc.), and the input line is long and the load surface is insufficient, the voltage of the load is seriously reduced, and it may be difficult to start the load; The output is instantaneously over-voltage and power-off. If such a phenomenon occurs, it is not a voltage regulator failure. The input line should be improved (the line should be thickened, and the length of the input line should be shortened as much as possible to reduce the voltage drop in the line).
11. When the output voltage of the voltage stabilizer is seriously deviated from 220V, check ① whether the input voltage is within the voltage regulation range; ② whether the motor gear is seriously worn and whether the rotation is flexible; ③ whether the limit switch is damaged; ④ whether the coil plane is smooth; ⑤ Whether the control board is damaged
Regulator safety matters:
1. When the regulated power supply is powered on, please do not disassemble the regulated power supply or pull the input and output wiring of the regulated power supply at will to prevent electric shock or other electrical safety accidents.2. The input and output connections of the regulated power supply must be arranged reasonably to prevent treading and abrasion, resulting in leakage accidents.
3. The regulated power supply must be grounded reliably. The user is responsible for the electric shock or personal injury caused by the operation of the ungrounded wire.
4. The ground wire of the regulated power supply cannot be connected to public facilities such as heating pipes, water supply pipes, gas pipes, etc., so as not to infringe the rights of third parties or cause harm.
5. The input and output wiring of the regulated power supply should be checked regularly to avoid loosening or falling off, thus affecting the normal use of the regulated power supply and the safety of electricity use.
6. The selection of the connecting line of the voltage stabilizer must reach the connecting line that can carry enough current capacity.
7. The voltage stabilizer should be handled with
care, and avoid violent vibration during work; 8. Ensure that the carbon brush spring of the voltage stabilizer has sufficient pressure to prevent the contact surface between the carbon brush and the coil from sparking;
9. Non-professionals please Do not disassemble or repair the regulated power supply.
Voltage stabilizer capacity selection:
First of all, it depends on what type of electrical equipment you are using. Generally, the load is not purely resistive. Therefore, in the actual selection, the regulated power supply should be reasonably selected according to the specific conditions of the rated power, power factor and load type of the electrical equipment, and an appropriate margin should be reserved for its output power, especially when the impact load is selected. If it is larger, the specific selection is as follows:1. For pure resistive loads such as incandescent lamps, resistance wires, electric furnaces and other equipment, the power of the voltage stabilizer should be 1.5 times to 2 times the power of the load equipment.
2. Inductive and capacitive loads such as fluorescent lamps, fans, motors, pumps, air conditioners, computers, refrigerators, etc. The power of the voltage regulator should be 3 times the power of the load device.
3. In the case of large inductive and capacitive loads, the starting current of the load should be considered particularly large (up to 5~8 times of the rated current) when selecting the model, so the power of the voltage stabilizer should be more than 3 times the load power.
The difference between voltage stabilizer and UPS:
Voltage stabilizer and UPS are different concepts, but many friends always mistakenly think that voltage stabilizer is UPS, which is essentially different; UPS is divided into online type and backup type. Generally, the computer is equipped with a backup type. It belongs to a kind of emergency power supply; the backup type is a kind of electronic switching regulator with a voltage stabilizer, which can be used as a voltage stabilizer, but the voltage stabilization effect is not ideal; voltage stabilizer: it is used for voltage instability It is designed mainly for the protection of back-end equipment, and the protection function of the equipment is relatively complete. Generally, large-scale UPS must also be equipped with a voltage regulator bypass system, that is, LW-PLG voltage regulator. The concept of a voltage regulator is introduced above. What is a UPS here? The Chinese meaning of UPS is "uninterruptible power supply", which is the English "Uninterruptible Power".Analysis, summary and elimination of failure performance reasons
No output, no voltage indication or no startup
1, the overvoltage or undervoltage protection 1, the output voltage of the internal regulator adjustable potentiometer2, out of phase 2 and the phase protection, any exchange of three-phase two-phase
3, the main control circuit board 3 is broken, replacing
4, the output Communication is broken 4. Replace
The output voltage is abnormal
1. It is a coherent regulator 1. Replace the sub-regulated regulator2. Exceed the voltage regulation range of the regulator itself 2. Replace the wide-range regulator
3. The travel limit switch is broken 3. Replace
4. Phase circuit board Damaged 4. Replacement
5. Servo motor burnt 5. Replacement
Unregulated
1. Exceeds the voltage stabilization range of the voltage stabilizer itself (replace the wide-range voltage stabilizer)2. The travel limit switch is damaged (replace)
3. The circuit board is damaged (replace)
4. The servo motor is burnt (replace)
Trip for no reason at work
1. The selection of the total gate capacity is too small (replace the air switch with a suitable capacity)2. The air switch is broken (replace)
3. The surge voltage is instantaneously too high (replace the non-contact high-precision voltage stabilizer)
There is a loud humming sound inside the regulator
1. The overload is loaded (reduce the equipment connected later)2. There are debris inside (remove the debris)
There is a loud squeak inside the regulator
1. The voltage is unstable 1. Normal2. There is dust on the surface of the carbon brush 2. After removing the dirt
Regulator does not operate automatically
1. The automatic button switch is not turned on 1. Turned on2. The circuit board is faulty 2. Replacement
Press the panel to boost and boost without boost or buck (non-power regulators do not have this function)
1, the servo motor burned 1, replacing2, 2 travel limit switch is bad, replace
3, burned circuit board 3, replacing
4, manual and automatic to a manual knob 4 is not open, open to a manual
Tips: if the voltage regulator When there is a fault, you cannot eliminate it, and you cannot stop the power supply to the back-end equipment; please contact a professional company.
The role of the voltage stabilizer
The voltage stabilizer is a power supply circuit or power supply equipment that can automatically adjust the output voltage. The function of the voltage stabilizer is to stabilize the power supply voltage that fluctuates greatly and does not meet the requirements of electrical equipment within its set value range, so that various circuits can be stabilized. Or the electrical equipment can work normally under the rated working voltage. All regulators use the same technique to stabilize the output voltage. The output voltage is sampled by a voltage divider resistor connected to the inverting input of the error amplifier. The non-inverting input of the error amplifier is connected to a reference voltage Vref. Let's take a look at the role of the voltage regulator. The original power regulators relied on the beating of relays to stabilize the voltage. When the grid voltage fluctuates, the automatic correction circuit of the power regulator is activated to make the internal relay operate. Forcing the output voltage to remain near the set value, the advantage of this circuit is that the circuit is simple, but the disadvantage is that the voltage regulation accuracy is not high, and every time the relay jumps and shifts, it will cause an instantaneous interruption of the power supply and spark interference. In the later period and now, the voltage stabilizer is generally an industrial-grade voltage stabilizer. The industrial-grade voltage stabilizer uses the induction principle to adjust the voltage, and the voltage is adjusted linearly in the load without contact. During the voltage adjustment, there will be no frequency deviation. The power quality of the load is the same as that of the input terminal. It is composed of industrial grade parts with high efficiency and wide safety range, which can withstand harsh temperature, humidity, vibration and dirty environment. The voltage regulator is mainly composed of a voltage regulation circuit, a control circuit, and a servo motor. When the input voltage or load changes, the control circuit performs sampling, comparison, and amplification, and then drives the servo motor to rotate, so that the position of the voltage regulator carbon brush changes. , by automatically adjusting the coil turns ratio to keep the output voltage stable. The voltage stabilizer with larger capacity also works on the principle of voltage compensation. With the rapid development of society, electrical equipment is increasing day by day. However, due to the aging and development lag of power transmission and distribution facilities, as well as poor design and insufficient power supply, the voltage of end users is too low, while the voltage of line users is often too high. And sophisticated equipment, like a time bomb. When it comes to the role of the voltage stabilizer, as a public power grid, the mains system is connected to thousands of various loads, some of which are larger inductive, capacitive, switching power supplies and other loads not only obtain electrical energy from the grid, but also In turn, it will have an impact on the power grid itself, deteriorating the power grid. The power supply quality of the grid or local grid, resulting in the distortion of the mains voltage waveform or frequency drift. In addition, unexpected natural and man-made accidents, such as earthquake, lightning strike, open circuit or short circuit of power transmission and transformation system, will endanger the normal supply of electricity, thus affecting the normal operation of the load. According to the tests of electric power experts, the problems that often occur in the power grid and cause interference or damage to computers and precision instruments mainly include the following: 1. Power surges: Refers to the output voltage RMS value is higher than the rated value of 110%, and Duration of one or more cycles. Surge is mainly due to the high voltage generated by the sudden unloading of the grid when the large electrical equipment connected to the grid is shut down. 2. High voltage spikes: refers to the voltage with a peak value of 6000v and a duration from 1/10,000th of a second to 1/2 cycle (10ms). This is mainly due to lightning strikes, arcing, static discharges or switching operations of large electrical equipment. 3. Switching transients: refers to the pulse voltage with a peak voltage of up to 20,000V, but a duration of between one millionth of a second to one millionth of a second. The main causes and possible damage are similar to high-voltage spikes, but the solution is different. 4. Voltage sag (power sags): refers to the low-voltage state in which the effective value of the mains voltage is between 80% and 85% of the rated value, and the duration is one to several cycles. This problem can be caused by the startup of large equipment, the startup of large electric motors, or the connection of large power transformers. 5. Electrical line noise: refers to radio frequency interference (RFI), electromagnetic interference (EFI) and other high-frequency interference. The operation of the motor, the action of the relay, the operation of the motor controller, the broadcast emission, the microwave radiation, and the electrical storm, etc., will cause line noise interference. 6. Frequency variation (frequency variation): refers to the variation of the mains frequency exceeding 3Hz. This is mainly caused by the unstable operation of the emergency generator, or by the power supply with unstable frequency. Unstable voltage will cause fatal injury or malfunction of the equipment, affect production, cause delay in delivery, unstable quality and other losses. At the same time, it accelerates the aging of the equipment, affects the service life and even burns the accessories, so that the owner faces the trouble of needing maintenance or needs to update the equipment in the short term, wasting resources; In severe cases, safety accidents may even occur, resulting in immeasurable losses. Voltage stabilizers are essential for electrical equipment, especially high-tech and precision equipment with strict voltage requirements, which also prompts us to develop high-tech and more advanced voltage stabilizers to meet the requirements of various instruments and equipment. demand. Therefore, we should know the use of voltage regulators, and we should also understand the role of voltage regulators.Regulator parameter metrics and technical parameters:
Voltage stabilizer technical parameters ∣ voltage stabilizer parameter measurement standard 1. The voltage stabilizer has an adaptable range of input voltage. The IEC standard is for the input voltage to vary within ±10% of the rated value. The input range of our products is ±20%; the maximum can be ±50%. If it exceeds the range of undervoltage and overvoltage, it will automatically alarm with sound and light, and the output voltage cannot be stabilized within the required range. 2. The output voltage regulation rate is the effect of the output change caused by the change of the input voltage. When the load is at the rated value, the input voltage is adjusted upward from the rated value to the upper limit value and the lower limit value according to the source voltage range. Measure The maximum variation of the output voltage (single-phase 220V±10%). The smaller the value, the better, and is an important indicator to measure the performance of the AC voltage stabilizer. 3. Load regulation rate: It is the effect of the change of the load caused by the change of the output. Change the load current and measure the change (±8%) of the output voltage. The smaller the value, the better, and it is also an important indicator to measure the performance of the AC voltage stabilizer. 4. The relative harmonic content of the output voltage (also known as the output voltage distortion), usually expressed by THD, is the ratio of the total rms value of the harmonic content to the fundamental rms value. When the load is the rated value, the input voltage distortion satisfies the reference When the conditions are met (generally should be less than 3%), measure the output voltage distortion when the input voltage is the lowest value, the rated value and the highest value, whichever is the largest. The smaller the value, the better. (Liwei series voltage stabilizer is less than 1%; the power voltage stabilizer has no harmonic content) 5. Efficiency: It is the ratio (percentage) of the output active power P0 to the input active power Pi. 6. Load power factor. The capacity of the voltage regulator is expressed in volt-ampere (VA) or kilovolt-ampere (KVA) value. In addition to purely resistive loads, there are also inductive and capacitive loads in the load, that is, in addition to active power, there are work power. This pointer reflects the ability of the AC regulated power supply to carry inductive and capacitive loads. In general AC regulated power supply, the load power factor cosφ is 0.8. When the product is 1KVA, the maximum output active power (that is, the capacity with resistive load) is: 800W. If the product is expressed in 1KW (cosφ is still 0.8), Active power can be output 1KW, at this time the output power S=1000/0. 8=1250VA. When the value of the load power factor is small, it means that the power supply equipment has a strong ability to adapt to reactive loads. 7. The parameters of the AC voltage stabilizer include output power, input frequency, source frequency effect, random deviation (time drift), no-load input power, and source power. Factors (this value is different from the load power factor, the bigger the better, the maximum is 1), the relative harmonic content of the source current, the audio noise and other items, the three-phase AC regulated power supply, and the three-phase output voltage unbalance, etc. For the definition of indicators and test methods, please refer to relevant industry standards.How to repair and maintain the voltage stabilizer:
The general maintenance and inspection items of the voltage stabilizer are as follows:
1. Whether the voltage stabilizer still has design and installation defects;
2. Check whether the load current and operating voltage of the voltage stabilizer are normal;
3. Check whether the regulator has oil leakage, whether the oil level, oil color, and temperature exceed the allowable values. The oil temperature of the upper layer of the oil-immersed self-cooling regulator is generally below 85 °C, and the strong oil is air-cooled and the strong oil is water-cooled. The voltage regulator should be below 75℃;
4. Check whether the high and low voltage porcelain bushings of the voltage stabilizer are clean, and there are no cracks, damages and traces of flashover discharge;
5. Check whether the terminals of the voltage stabilizer are in poor contact and overheating;
6. Check whether the operating sound of the voltage stabilizer is normal; there is a uniform humming electromagnetic sound during normal operation. If there is a crackling discharge sound inside, it may be the breakdown of the winding insulation. If there is uneven electromagnetic sound, it may be The core bolt or nut of the iron core is loose.
7. Check whether the hygroscopic agent of the voltage stabilizer is saturated;
8. Check whether the oil cut valve of the voltage regulator is normal, and whether the cut door leading to the gas relay and the cut door of the radiator are open;
9. Check whether the diaphragm of the explosion-proof tube of the voltage stabilizer is complete, and whether the diaphragm glass is marked with a "cross";
10. Check whether the cooling device of the voltage stabilizer is operating normally, whether the temperature of the cooling pipe is uniform, and whether there is any blockage of the oil pipe;
11. Check whether the housing of the voltage stabilizer is well grounded;
12. Check whether the gas relay is full of oil and whether there is gas;
13. For outdoor voltage stabilizers, focus on checking whether the foundation is in good condition and whether the foundation sinks. For the changing pole, check whether the pole is firm, and whether the wooden pole and the root of the pole are corroded.
14. For the indoor voltage stabilizer, focus on checking whether the doors and windows are in good condition, and check whether the blind wire gauze is complete;
The difference between a voltage regulator and a transformer:
We know that electricity can generate magnetic fields, and magnetic fields can also be converted into electricity. When one coil is connected to alternating current, an alternating magnetic field will be generated, and then the alternating magnetic field will pass through another coil, and a voltage will be induced on the other coil. This is the principle of a transformer. The number of turns of each coil is related; to put it simply, the transformer uses the principle of magnetic coupling and is composed of primary and secondary windings (coils). The voltage across the coil is proportional to the number of turns of the coil, so the number of turns of the primary and secondary coil The ratio determines the transformation ratio of this transformer. Obviously, the transformer has no voltage regulation function, because the secondary voltage changes with the primary voltage.The voltage stabilizer uses the principle of negative feedback. For example, open the tap of the tap water to half, and install a sensor at the outlet of the tap to detect the amount of water. If the amount of water is large, it will automatically If the water output is small, it will automatically turn on the faucet to keep the water output constant. The principle of the voltage stabilizer is roughly the same. There is a circuit in the voltage stabilizer that can detect the change of the output voltage (the voltage divider resistance sampling circuit at the inverting input of the error amplifier, this circuit can now be reduced to only one integrated chip), when the output voltage When changing, the circuit that detects the change of the output voltage is provided by the chip to provide feedback to the private server motor, and then the private server motor drives the arm to automatically adjust the position of the brush, so as to stabilize the output voltage. This is the simplest voltage stabilizer. To sum up, the transformer has no function of voltage regulation, but the negative feedback technology can be used to design a transformer with voltage regulation, which is no problem, but this is not the case with general transformers. The output voltage of the transformer does not change much within a certain range of use, and it is not a concept with what we call voltage regulation.
All regulators use the same technique to stabilize the output voltage. The output voltage is sampled through a voltage divider resistor connected to the inverting input of the error amplifier, whose non-inverting input is connected to a reference voltage. The error amplifier is always trying to force the inputs to be equal across it. To do this, it provides load current to keep the output voltage stable (that is, negative feedback)
Supplementary knowledge:
There are many types of voltage stabilizers. Common voltage stabilizers are: automatic AC voltage stabilizer, purified power supply AC voltage stabilizer, parameter voltage stabilizer, high-power compensation power stabilizer, non-contact intelligent stabilized power supply . The electromechanical system of the telecommunications sector is a modern management realized through modern electronic technology and equipment. It involves communication technology, electronic technology, automatic control, computer technology and other disciplines, and has the characteristics of technology-intensive, high-tech, and high-performance. Power supply is the foundation of electromechanical equipment. If there is a problem with the power supply, it will bring a series of problems and even interruptions. Therefore, in reality, electricity consumption puts forward strict requirements on many equipment, including imported equipment and other precision instruments. In order to improve the reliability of the power supply system, relevant departments have added corresponding voltage stabilizers, stabilized power supplies, high-power Compensated power regulators are widely used in power distribution due to their economical and practical advantages.


 Industry Information
Industry Information